Navigating the Mediterranean Diet Basics
Understanding the Mediterranean Diet Principles
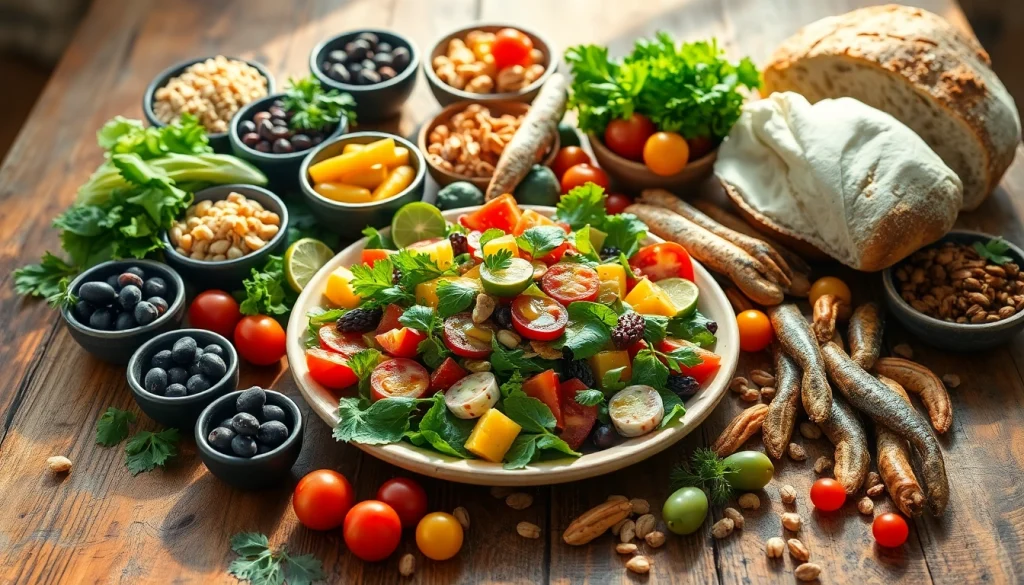
The Mediterranean diet is a unique approach to eating that’s deeply rooted in the traditional dietary habits of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes the consumption of whole, minimally processed foods, an abundance of plants, and fats primarily from healthy sources. Central to the Mediterranean diet is the idea of balance and moderation, fostering a nutritious yet enjoyable food experience.
This dietary pattern promotes the intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds while limiting red and processed meats and sugars. A noteworthy characteristic of the Mediterranean diet is its reliance on healthy fats, primarily from extra virgin olive oil, which serves as a staple in dishes and cooking methods. Additionally, fish and poultry are favored over red meats, underscoring a population-wide focus on healthier protein sources. For those looking to transform their dietary habits, diving into the mediterranean diet can be an excellent starting point.
Key Foods in the Mediterranean Diet
Understanding the food groups that constitute the Mediterranean diet is crucial for anyone looking to adopt this dietary pattern. Here’s a breakdown of the key food categories:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colorful options daily. Fresh produce should comprise a substantial part of each meal.
- Whole Grains: Foods like whole wheat bread, oats, and brown rice serve as staples, providing essential fiber and nutrients.
- Legumes and Nuts: Beans, lentils, and a variety of nuts offer plant-based protein and healthy fats, essential for heart health.
- Fish and Seafood: Aim for two servings per week, focusing on fatty fish like salmon and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Poultry and Eggs: These should be consumed in moderation, offering additional protein options without the higher saturated fats found in red meats.
- Dairy: Opt for low-fat or fermented varieties like yogurt and cheese, which are great sources of calcium without excessive calories.
- Herbs and Spices: Using fresh herbs and spices instead of salt enhances flavor while providing various health benefits.
- Healthy Fats: Extra virgin olive oil is the primary fat, accompanied occasionally by other oils such as avocado oil.
Benefits of Adopting the Mediterranean Diet
Research consistently highlights various benefits related to following the Mediterranean diet. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
- Heart Health: Studies have shown that this diet can lower cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: By emphasizing whole foods and healthy fats, the Mediterranean diet encourages sustainable weight loss and maintenance.
- Diabetes Management: The diet’s focus on low glycemic index foods promotes stable blood sugar levels, making it easier to manage diabetes.
- Brain Health: Evidence suggests a link between this diet and reduced cognitive decline, as well as a lower risk of diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Mental Wellbeing: The Mediterranean diet has been found to enhance mood and decrease the risk of depression due to its rich nutrient content.
Meal Planning for the Mediterranean Diet
Creating Your Mediterranean Diet Grocery List
Adopting the Mediterranean diet requires a well-thought-out grocery list to ensure you have all the necessary ingredients. Here’s a comprehensive grocery list to get you started:
- Fresh Produce: Apples, oranges, spinach, tomatoes, bell peppers, zucchini, and onions.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, barley, whole grain bread, and brown rice.
- Legumes: Canned or dried chickpeas, lentils, kidney beans.
- Fish and Seafood: Canned tuna, salmon, and fresh shrimp.
- Poultry: Chicken breast and eggs.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and sunflower seeds.
- Dairy: Greek yogurt and feta cheese.
- Healthy Fats: Extra virgin olive oil and avocado oil.
- Herbs and Spices: Basil, oregano, garlic, cumin, and paprika.
Sample Weekly Meal Plan for the Mediterranean Diet
A structured meal plan can simplify your transition into the Mediterranean diet. Here’s a sample weekly meal plan that illustrates how to incorporate these foods into your daily routine:
Day 1
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt topped with honey, walnuts, and berries.
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with cherry tomatoes, cucumber, and feta cheese drizzled with olive oil.
- Dinner: Grilled salmon with a side of steamed broccoli and brown rice.
Day 2
- Breakfast: Whole grain toast with smashed avocado and poached eggs.
- Lunch: Lentil soup with a side salad dressed in olive oil and vinegar.
- Dinner: Chicken Marbella (marinated with olives and prunes) served with roasted sweet potatoes.
Day 3
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with almond milk, chia seeds, and sliced bananas.
- Lunch: Hummus wrap with mixed greens, cucumbers, and carrots.
- Dinner: Mediterranean pasta with whole grain penne, spinach, artichokes, and feta cheese.
Day 4
- Breakfast: Smoothie with spinach, banana, Greek yogurt, and sunflower seeds.
- Lunch: Chickpea salad with red onion, parsley, and lemon dressing.
- Dinner: Grilled shrimp skewers with a side of tabbouleh.
Day 5
- Breakfast: Feta and spinach omelet with whole grain toast.
- Lunch: Caprese salad with mozzarella, tomatoes, and basil.
- Dinner: Beef stew with chickpeas and spices served with whole grain bread.
Day 6
- Breakfast: Muesli with fruit and yogurt.
- Lunch: Falafel wrap with tahini sauce and mixed vegetables.
- Dinner: Baked eggplant with tomatoes and mozzarella.
Day 7
- Breakfast: Smoothie bowl with mixed berries and nuts.
- Lunch: Spinach and beet salad with goat cheese.
- Dinner: Whole grain pizza topped with vegetables and a light sprinkle of cheese.
Tips for Meal Prep on the Mediterranean Diet
Meal prepping is an effective strategy for adhering to the Mediterranean diet, especially for busy lifestyles. Here are some tips to make meal prep easier and more effective:
- Batch Cooking: Prepare larger amounts of grains and legumes at the start of the week for easy incorporation into meals.
- Use Versatile Ingredients: Foods like roasted vegetables, grilled chicken, and prepared quinoa can be used in various dishes throughout the week.
- Invest in Quality Containers: Durable containers will help keep your meals fresh and easy to transport.
- Plan Ahead: Take time each week to plan meals and snacks, making grocery shopping more straightforward.
- Label and Date: Clearly label your prepped meals with contents and date to ensure freshness and avoid waste.
Health Benefits Associated with the Mediterranean Diet
Cardiovascular Health and the Mediterranean Diet
Numerous research studies indicate that adhering to the Mediterranean diet significantly benefits cardiovascular health. Consuming heart-healthy fats—such as those found in olive oil, fatty fish, and nuts—helps to lower bad cholesterol levels and reduce inflammation. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contributes essential antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that are crucial for heart health.
It is recommended that people aiming to improve their heart health focus on the Mediterranean diet as it is correlated with a reduced risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases. Regular inclusion of fish, particularly oily fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, provides essential fats that support heart function and overall cardiovascular wellness.
The Influence of the Mediterranean Diet on Weight Management
The Mediterranean diet encourages a balanced approach to eating, which can be ideal for those looking to manage their weight. Its emphasis on high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes satiety and reduces the likelihood of overeating. Moreover, the focus on healthy fats can help regulate hunger hormones, leading to a natural decrease in calorie consumption without strict restrictions.
Long-term studies suggest that transitioning to a Mediterranean diet can lead to sustainable weight loss and improved body composition, making it a practical choice for weight management. Additionally, the diet encourages a positive relationship with food, reducing the likelihood of yo-yo dieting.
Improving Mental Health with the Mediterranean Diet
Emerging research suggests that the Mediterranean diet may have beneficial effects on mental health. Nutrient-rich foods, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins found in plant-based foods, play a critical role in brain health. The reduction of processed foods and added sugars processes support cognitive function, potentially lowering the incidence of depression and anxiety.
Some studies indicate that individuals who diligently follow the Mediterranean diet report a greater sense of overall well-being and happiness. Furthermore, shared meals, a hallmark of Mediterranean culture, can enhance social connections that are important for mental health.
Best Practices for Following the Mediterranean Diet
Integrating Mediterranean Diet in a Busy Lifestyle
Transitioning into the Mediterranean diet can feel challenging; however, with some strategic planning, it can seamlessly fit into a busy lifestyle. Here are practical tips to incorporate this diet into your routine:
- Start Small: Begin by replacing one meal a day with Mediterranean-inspired options, gradually expanding as you become comfortable.
- Stock Up on Staples: Keep essential Mediterranean ingredients on hand for quick and easy meals—canned beans, frozen vegetables, and whole grains can save time.
- Opt for Simple Recipes: Choose straightforward recipes that require minimal preparation and cooking time to ease into this eating pattern.
- Plan for Leftovers: Prepare a little extra during your meal prep, so you have quick and healthy meals readily available for busy days.
Common Misconceptions about the Mediterranean Diet
Despite the increasing popularity of the Mediterranean diet, several misconceptions may hinder individuals from adopting this healthful pattern. Here we address common myths:
- Only for Weight Loss: While great for weight management, the Mediterranean diet is primarily designed for overall well-being, not just weight loss.
- It’s Expensive: Contrary to popular belief, many staples of the Mediterranean diet such as grains, legumes, and fruits are budget-friendly.
- Too Restrictive: The Mediterranean diet is flexible, allowing for a variety of foods and occasional indulgences.
Sustainable Eating Experience with the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is not just a meal plan—it’s a lifestyle choice that promotes sustainable eating habits. The principles of this diet emphasize seasonal and local foods, encouraging consumers to buy fresh produce and make environmentally conscious food choices. By prioritizing plant-based foods and organic options, individuals contribute to a more sustainable food system.
Moreover, the Mediterranean lifestyle encourages communal dining and shared meals, fostering relationships and a sense of community. This social aspect of eating not only enhances the dining experience but also improves mental health and emotional well-being.
Advancing Your Knowledge of the Mediterranean Diet
Exploring Regional Variations in the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean region is culturally and geographically diverse, which is reflected in the variations of the Mediterranean diet across different countries. For example, the Italian version may emphasize pasta and cheese, while the Greek variety might focus on olives and seafood. Exploring these regional differences can deepen your appreciation for the diet and expand your repertoire of recipes.
Consider trying recipes from various Mediterranean countries. Learning about their traditional dishes can provide insight into the cultural significance of food and enhance your culinary skills.
Adapting the Mediterranean Diet to Dietary Restrictions
Adopting the Mediterranean diet doesn’t mean compromising on personal dietary restrictions or preferences. Here’s how to adapt:
- Vegetarian/Vegan: Emphasize plant-based proteins from legumes and tofu, and replace cheese and dairy with plant-based alternatives.
- Gluten-Free: Focus on whole grains like quinoa and brown rice while avoiding traditional wheat products.
- Dairy-Free: Enjoy nut-based cheeses and yogurts that align with Mediterranean flavors.
Resources for Further Learning about the Mediterranean Diet
Understanding the Mediterranean diet is a journey that can be enriched through various resources:
- Books: Look for cookbooks focused on Mediterranean cuisine for recipes and techniques.
- Online Courses: Many platforms offer courses that delve into the principles and recipes associated with the Mediterranean diet.
- Cooking Classes: Participate in local cooking classes to learn traditional Mediterranean cooking methods and dishes.
- Nutritionist Guidance: Consulting a nutritionist can provide personalized advice tailored to your dietary needs and goals.